AWS Cost Reduction: From $22,000 to $6,300 with Practical Strategies
In the world of cloud computing, one of the biggest challenges for companies is keeping costs under control without sacrificing performance. In this article, I share the specific strategies we’ve implemented to reduce our AWS infrastructure costs from $22,219 to $6,334 per month, nearly 70% in savings.
The Starting Point: A Historical High of $22,219
In January 2023, our AWS bill reached its historical high: $22,219.16. Our infrastructure had grown organically over time, resulting in a very high monthly bill that didn’t necessarily correspond to our actual needs.
The main problem? Lack of cost visibility and strategy. We had resources we were paying for without using, oversized instances, and an architecture that hadn’t been reviewed with a cost focus.
Optimization Strategies Implemented
After a comprehensive analysis of our infrastructure, we implemented a series of strategies that have significantly reduced our monthly bill.
1. Databases: RDS Reserved Instances
One of the most immediate improvements was migrating our RDS instances to the reserved instance model.
Before: On-Demand Instances
- Monthly cost: $2,200
After: Reserved Instances (1 year, Standard, No Upfront)
- Monthly cost: $1,100
- Savings: 50% ($1,100 monthly)
This change was immediate with no performance impact, simply by committing to using the same instance size for one year.
2. DynamoDB: Provisioned Capacity Review
Many DynamoDB tables had provisioned read/write units that were no longer being used.
Actions taken:
- Deactivate unnecessary read/write unit reservations
- Migrate low-usage tables to “On-Demand” billing mode
- Delete obsolete tables
Result: Significant savings by eliminating payment for unused capacity.
3. EC2 and EKS: Spot Instances and Saving Plans
For computational processes, we implemented a mixed strategy:
Spot Instances
For non-critical processes that tolerate interruptions, such as:
- Non-urgent batch processes
- Development and testing environments
- Non-critical data analysis jobs
Savings: Up to 70-90% compared to On-Demand instances
Saving Plans
For the vast majority of instances running 24x7 requiring guaranteed availability:
- Production web servers
- Critical workers
- Essential architecture components
Savings: Average of 50-60% compared to On-Demand
Graviton Instances
Migration to ARM-based instances (Graviton) whenever possible:
- Better price/performance ratio
- Structurally more economical
- Compatible with most workloads (especially the EKS cluster)
Savings: Additional 20-30% compared to equivalent x86 instances
4. Orphaned Resources: Infrastructure Cleanup
One of the most surprising discoveries was the amount of resources we were paying for without using:
Resources removed:
- EBS Volumes: Disconnected and forgotten
- CloudWatch Log Groups: With infinite retention and no queries
- S3 Buckets and objects: Obsolete data and old backups
- Load Balancers: ELB/NLB not associated with any active target group
Cleanup process:
- Automation with orphaned resource detection scripts
- Manual review of each detected resource
- Safe deletion with retention policies
Savings: Hundreds of dollars monthly on resources no one was using.
5. Networking: VPC and Public IP Optimization
The network architecture also had significant hidden costs:
VPC Peering:
- Network centralization with VPC Peering
- Reduction of redundant NAT Gateways
- Traffic optimization between VPCs and availability zones
Public IP Reduction:
- Elimination of unnecessary elastic IPs
- Migration to PrivateLink whenever possible
- Use of VPC endpoints for AWS services
Result: Significant reduction in network costs.
6. Infrastructure as Code: Terraform Management
A fundamental change was managing all infrastructure and environments with Terraform:
Benefits:
- Complete visibility of all resources
- Detection of unmanaged resources
- Easy elimination of entire environments (dev, staging)
- Prevention of “resource drift”
- Change review via code review
Impact: Continuous improvement in infrastructure efficiency.
Global Results
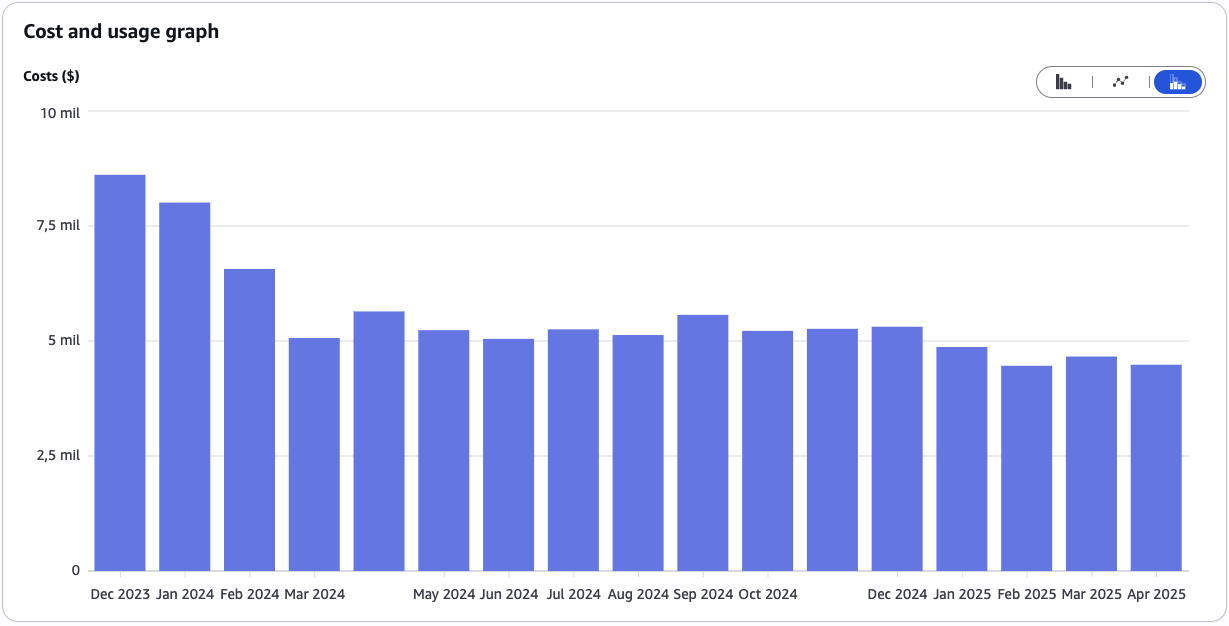
After implementing all these strategies progressively during 2023 and 2024, the results have been very significant:
Economic Impact
- Initial bill (Jan 2023): $22,219.16
- Current bill (Apr 2025): $6,334.28
- Total cost reduction: 69.4% savings
- Monthly savings: $15,884.88
- Annual accumulated savings: Nearly $200,000
Operational Improvement
Beyond economic savings, we’ve achieved significant improvements:
- Visibility: Exact knowledge of what resources we have and what they’re for
- Control: Ability to predict and control the monthly bill
- Efficiency: Fewer resources, same (or better) processing capacity
- Cost culture: Team awareness of the impact of technical decisions on costs
Lessons Learned
1. Consistency is Key
Cost optimization is not a one-time project but a continuous process. Platform needs change and infrastructure must adapt.
2. Automate Detection
Orphaned resource detection scripts are essential. Humanly, it’s impossible to maintain control without automation.
3. Review Periodically
We established quarterly reviews of:
- Instances and their utilization
- Databases and their size
- Storage and retention optimization
- Traffic and usage patterns
This allowed us to go from $22,219 in January 2023 to $12,977 in December 2023, and reach the historical low of $6,334 in April 2025.
4. Infrastructure as Code is Mandatory
You can’t optimize what you don’t know. Terraform (or equivalent IaC) is essential to maintain control.
5. Not All Savings Are Worth It
You must evaluate implementation cost vs resulting savings. Some optimizations require a lot of effort for minimal savings.
Conclusion
AWS cost reduction is not magic, but a combination of visibility, strategy, and consistency. The techniques described in this article - reserved instances, spot instances, Graviton, orphaned resource cleanup, network optimization, and infrastructure as code - have allowed us to reduce our bill by nearly 70%, from $22,219 to $6,334 monthly.
The journey hasn’t been linear: we went from $22,219 in January 2023 to $12,977 in December 2023, and reached the historical low of $6,334 in April 2025. Each optimization contributed its grain of sand, and the sum of all of them has made possible such a significant reduction.
If your AWS infrastructure has grown without a clear cost strategy, I encourage you to start with analysis: what you have, what you actually use, and what you can optimize. The results can be surprising, as demonstrated by our nearly $200,000 in annual savings.